A superabsorbent polymer (SAP) is a type of material with the ability to absorb and retain large amounts of liquid relative to its own mass. These polymers are used in various applications where moisture management or absorption is crucial, such as in diapers, feminine hygiene products, agriculture (for retaining water in soil), and even in medical settings for wound dressings.
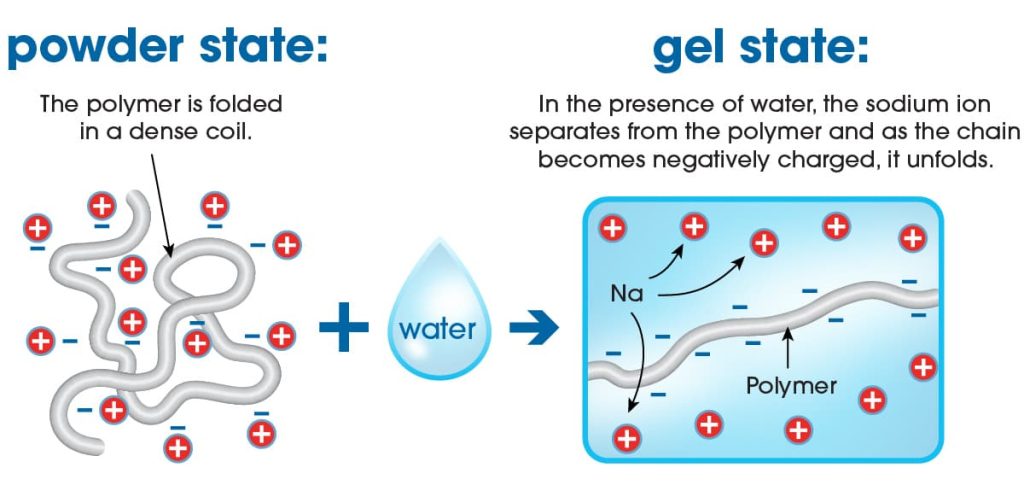
The unique properties of superabsorbent polymers stem from their structure, which typically involves cross-linked chains of molecules that can swell when they come into contact with water or other aqueous solutions. This swelling capacity allows them to absorb and retain water or other liquids effectively.
What are the Super Absorbent Polymer (SAP) type materials on the market?
There are several types of superabsorbent polymers (SAPs) available on the market, each with its own characteristics and uses. Some common types include:
Sodium polyacrylate:

This is one of the most widely used SAPs, especially in applications like diapers and feminine hygiene products. It has a high absorption capacity and can retain moisture effectively.
Potassium polyacrylate:
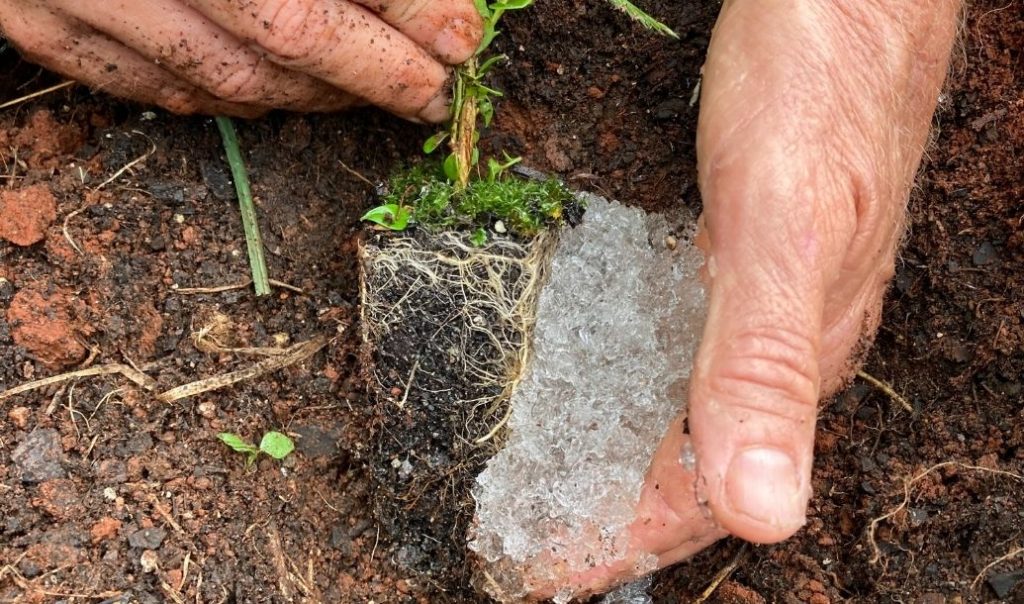

This is one of the most widely used SAPs as soil water retaining agents, especially in applications with severe soil moisture in drought and saline-alkali lands. It has a high absorption capacity, can effectively retain water, improve soil structure, and has the effect of controlled and slow release of fertilizer when added to fertilizers.
Polyacrylamide:
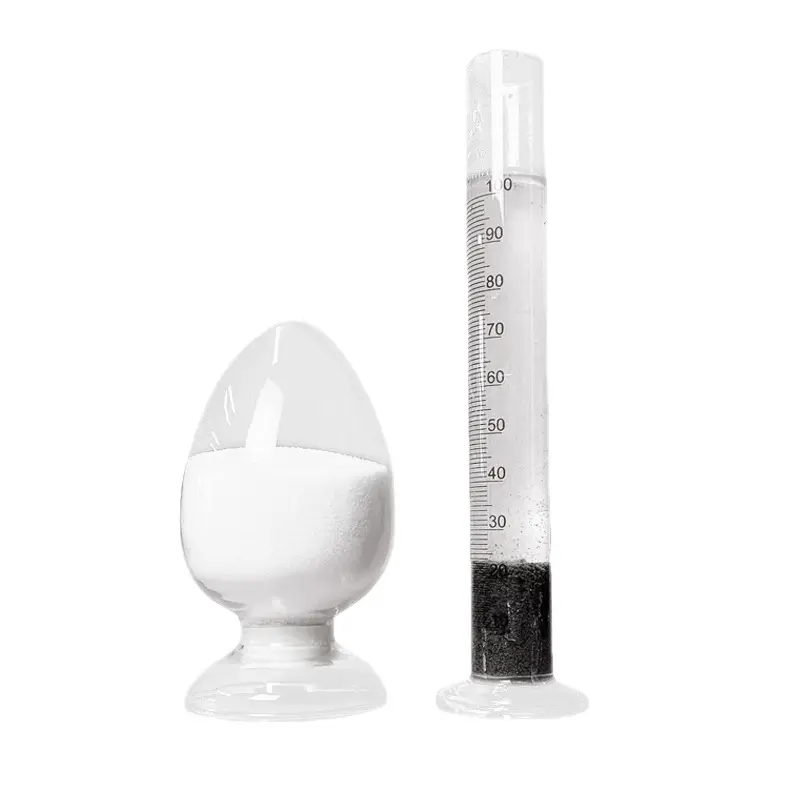

This type of SAP is often used in agriculture for soil conditioning and water retention. It helps improve soil structure and water holding capacity, leading to better plant growth.
Polyacrylic acid:
This SAP is commonly used in medical applications such as wound dressings. It has excellent absorption properties and can help keep wounds clean and moist for optimal healing.
Polyvinyl alcohol:
This type of SAP is used in applications where biodegradability is important, such as in environmentally friendly hygiene products or agricultural uses.
Modified starch-based SAPs:
These SAPs are derived from natural starch sources and are used in various applications, including food packaging, hygiene products, and agriculture.
These are just a few examples, and there are other variations and combinations of polymers used as superabsorbents depending on the specific requirements of the application.

